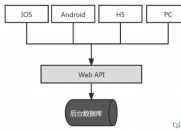
请使用QQ关联注册PLM之家,学习更多关于内容,更多精彩原创视频供你学习!
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?注册
x
最全的c++map的用法此文是复制来的0.0 1. map最基本的构造函数;
$ Q, t" m+ y' \map<string ,int>mapstring; map<int,string >mapint;, p1 _5 m" R/ G( ?
map<sring,char>mapstring; map< char ,string>mapchar;, G2 j" L |) D# r8 n- E
map<char,int>mapchar; map<int ,char>mapint; 2. map添加数据; map<int ,string>maplive;1 H9 I% s3 n5 x7 y, ~
1. maplive.insert(pair<int,string>(102,"aclive"));
2 a4 j) E: F) E, ?! U: k8 N2. maplive.insert(map<int,string>::value_type(321,"hai"));
* O. N9 `# L4 c$ h5 @3. maplive[112]="April";//map中最简单最常用的插入添加!
/ s# Q% y1 E4 D4 v 3. map中元素的查找: find()函数返回一个迭代器指向键值为key的元素,如果没找到就返回指向map尾部的迭代器。 map<int ,string >::iteratorl_it;;
! C$ C. J3 n+ L6 a3 ^% V* fl_it=maplive.find(112);//返回的是一个指针
* `+ m! O6 o! B! V8 Jif(l_it==maplive.end())
! E, [( j6 `1 L( J" D, ncout<<"we do not find112"<<endl;
: W1 ?: w: d) l0 u7 ]2 J- g( Velsecout<<"wo find112"<<endl;
' z% {) u% ^- L+ u, i: f 0 w8 u' X2 x! ?6 ]
map<string,string>m; if(m[112]=="") cout<<"we do not find112"<<endl;* ^$ K* ?4 r7 w0 V% b: _7 g
4. map中元素的删除:
, a0 |. s, f0 a: P5 h, N如果删除112;+ ?( z9 S4 s# k0 z
map<int ,string>::iterator l_it;;
( M" j% _ I6 K# jl_it =maplive.find(112);
8 z: Z* X$ z* J2 N: Z! b4 E" ]" Sif( l_it == maplive.end())
/ a" N/ {1 ~: h. Kcout<<"we do not find112"<<endl;& n, Z# l8 w. E8 U, p6 i- D) Y5 }$ }
else maplive.erase(l_it);//delete 112;* v3 x- U; z# q% a: F
5. map中 swap的用法:2 C* z1 A& S! I4 ~ X+ R! B
Map中的swap不是一个容器中的元素交换,而是两个容器交换;
0 k! q D; D3 I# W5 v1 P; ], j4 IFor example:
2 ?! {1 h7 S# l7 u#include<map>
* H4 o0 H8 u* X0 U* \" r* g#include<iostream> usingnamespace std; int main()8 I' r* q9 @5 ~) R+ s
{
, k, x# B# Z+ y/ m! Z. u. x* Mmap <int, int> m1, m2, m3;% [/ E; w& m# I9 o) t6 R1 k
map <int,int>::iterator m1_Iter; m1.insert( pair <int, int>(1, 10 ) );* `2 }+ ~$ E8 r8 L
m1.insert ( pair <int,int> ( 2, 20 ) );/ h, _) c E5 j' @9 y/ x+ T/ r
m1.insert ( pair <int,int> ( 3, 30 ) );
+ o- F- F9 A8 {3 y1 j* }) |' [/ pm2.insert ( pair <int,int> ( 10, 100 ) );/ d3 m# v V; i4 b4 V5 M* V
m2.insert ( pair <int,int> ( 20, 200 ) );0 K0 ^$ h, F) b0 w
m3.insert ( pair <int,int> ( 30, 300 ) ); cout << "The original map m1is:";+ i* W0 A5 R+ W
for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ) ; m1_Iter != m1.end() ; m1_Iter++ )
, Y0 q# L/ R) y& |7 h7 J8 }cout << " "<<m1_Iter->second;. l% ?5 H+ z: ~& O8 j
cout << "."<< endl; // This isthe member function version of swap
3 D- p$ l4 k# [// m2 is said to be theargument map; m1 the target map; J; P( t4 Q# \+ Q6 n8 v5 i
m1.swap( m2); cout << "Afterswapping with m2, map m1 is:";
: @; e" R+ f" D$ d8 qfor ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ) ; m1_Iter != m1.end() ; m1_Iter++ )
- G% ^5 ~: l! {; [! T7 {cout << " "<< m1_Iter ->second;8 b; K9 l* U& p2 @3 [ m0 Y
cout << "."<< endl; * W" t: P2 X( \0 k8 E" w
cout << "After swapping with m2, mapm2 is:";
* h: O( T% T- A+ t2 C8 mfor ( m1_Iter = m2.begin( ); m1_Iter != m2.end(); m1_Iter++ )
. v" T, K+ z" G8 scout << " "<< m1_Iter ->second;' z; {7 C- v9 `+ h
cout << "."<< endl; 8 I8 s o+ R B9 d6 b+ ~ s
// This is the specialized template version of swap# r+ A) g3 g; U! K5 @( k
swap( m1, m3 ); cout << "Afterswapping with m3, map m1 is:";1 U0 ~; I+ j, r9 G/ B7 j
for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end(); m1_Iter++ )
* f3 F6 Z+ N; @1 |/ P7 Wcout << " "<< m1_Iter ->second;# N" l5 H# U( Q% F3 o
cout << "."<< endl;
: o M5 K5 j: ?, ]3 T( r5 n4 ]} 6. map的sort问题:
' o+ a N' \# G {" RMap中的元素是自动按key升序排序,所以不能对map用sort函数:
5 N% s, o. A- a6 MFor example:
1 |/ v( Z2 k: c#include<map>
" b2 [1 t2 h9 D" d3 `( m#include<iostream> usingnamespace std; int main( )
! y/ g8 q6 u) t; _6 n{
% e) J3 m3 B9 `6 H% }6 E& r% n1 Cmap<int, int> m1;7 R+ z: g5 z" _# H5 W) G
map <int,int>::iterator m1_Iter; m1.insert (pair <int, int> (1, 20 ) );
. l5 e1 e$ J; }: [, G7 e1 y3 U. o( Cm1.insert ( pair<int, int> ( 4, 40) );
# K5 _4 I, |# A( c: ~# h) O- L, U) Wm1.insert ( pair<int, int> ( 3, 60) );$ {% O3 R8 P5 }
m1.insert ( pair<int, int> ( 2, 50) );: L5 B) ^4 L: s- l( G
m1.insert ( pair<int, int> ( 6, 40) );
9 x" n% y% Y- G1 a! Jm1.insert ( pair<int, int> ( 7, 30) ); cout<< "The original map m1is:"<<endl;' L) o9 R, M K
for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( );m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
3 Q# ]9 E2 x$ }! E2 Icout << m1_Iter->first<<""<<m1_Iter->second<<endl;$ H# ~4 Z; Z# r4 O3 i
0 W9 J8 V+ p# V; m* j$ W8 w
}
1 s$ y: y" u r% @) j The original map m1 is:3 y$ g4 s+ B5 v$ t7 q8 z
1 20
' g& [: l7 K8 ^0 k+ y; p- w2 508 W/ {* Z+ B2 X+ d+ L
3 60
5 b- m1 Q, ~3 C% D9 ^) r* Z4 40
+ Y+ C/ k% E1 \3 Z6 40
( J$ }( R9 I% h/ j, G7 30 7. map的基本操作函数:
7 U+ a. b2 g% Z1 [C++Maps 是一种关联式容器,包含“关键字/值”对
$ e) J# x* a1 C3 O( }begin() 返回指向map头部的迭代器2 ^* l2 w+ a' l" a) x
clear() 删除所有元素7 f, {# d& d; S8 I8 |6 ?
count() 返回指定元素出现的次数
- Z/ @1 c& q( A7 X: x' _+ n1 {3 {empty() 如果map为空则返回true
# k M$ r5 B0 s; d9 Zend() 返回指向map末尾的迭代器3 e7 x0 \6 ?9 E+ w" z
equal_range() 返回特殊条目的迭代器对
$ M( g. t2 r- H8 j) S4 ?7 ferase() 删除一个元素( b, ^3 c9 V/ f; V
find() 查找一个元素& B5 U* ^) O% W. T- t% ?% ~# f' f+ R8 ~
get_allocator() 返回map的配置器
3 w6 M2 p) F x7 h* sinsert() 插入元素
( l1 O( |0 v" i( mkey_comp() 返回比较元素key的函数
4 \0 q3 K( v; Hlower_bound() 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置
/ |8 z: T, M+ O2 l$ R0 ]4 Mmax_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数2 I8 `0 o8 i) {) o9 ~- M6 B
rbegin() 返回一个指向map尾部的逆向迭代器
7 |; o |- ~# s" [$ V: Mrend() 返回一个指向map头部的逆向迭代器
8 ~+ h7 \8 ~9 psize() 返回map中元素的个数
) N3 m6 |- j6 t& Eswap() 交换两个map: \6 f; f0 w0 W5 o
upper_bound() 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置9 }" @( V. l/ G9 |+ m3 b
value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数 , q1 B; B y# I0 _: e
|